As the backbone of these cutting-edge lighting systems, the IC plays a pivotal role in enabling dynamic color-changing effects and individual pixel control.
Our in-depth exploration showcases a diverse array of popular models, shedding light on their unique features and functionalities.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an aspiring designer, or a seasoned professional, this article will provide valuable insights into the innovative world of addressable LED strip lights, specifically focusing on their key component, the Integrated Circuit (IC).
What is IC in Addressable LED Strip Lights?

In addressable LED strip lights, the Integrated Circuit (IC) stands as a pivotal component, enabling a mesmerizing array of color-changing effects that go beyond the capabilities of standard RGB modules. This sophisticated chip empowers each LED module with individual programming, granting unprecedented control over the display output.
VIDEO - Connection Guide on RGB and Addressable RGB LED
Through the IC’s ingenious design, LED strips can be seamlessly arranged in an array, with each chip possessing its distinct address or ID. This breakthrough feature facilitates the creation of captivating LED displays with unmatched precision and customization.
With remarkably low power consumption, the LEDs, governed by the IC, emit red, green, or blue light, resulting in a vast 256-bit color spectrum with a 5-bit brightness adjustment. The IC’s prowess lies in its ability to generate pulse width modulation output, which ensures a static screen, self-detection signal, and continuous oscillation support.
How Does IC in Addressable LED Strip Lights Function?
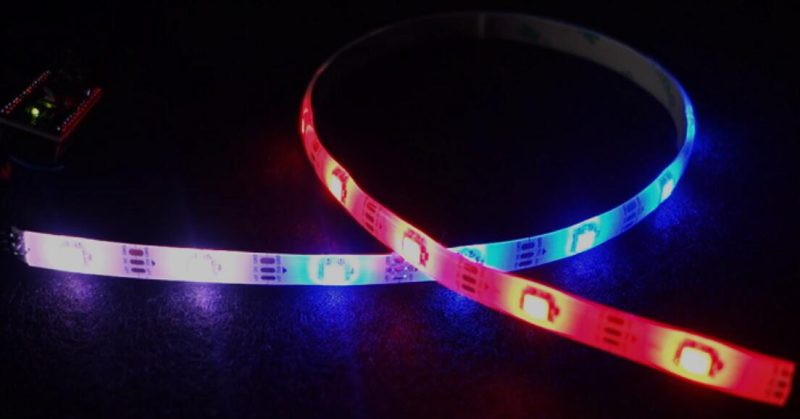

VIDEO - Individually Addressable LED Strips for Beginners
In Addressable LED Strip Lights, Integrated Circuit (IC) chips play a crucial role in enabling individual control and dynamic color-changing effects.
These chips are responsible for the intelligent and precise manipulation of each LED module, offering a captivating visual experience that goes beyond the capabilities of traditional LED strips.
Here’s a detailed explanation of how IC chips function in Addressable LED Strip Lights:
●Individual Addressing. The IC chips embedded within the LED strip allow each LED module to have its own unique address or ID. This individual addressing capability enables granular control over each LED, meaning that you can control them independently or in groups.
●Data Reception. The IC chip receives data signals from a microcontroller or other controlling devices. These signals contain instructions on the desired colors, brightness levels, and effects for each LED on the strip.
●Data Processing. Once the IC chip receives the data signals, it processes the information to interpret the commands for each LED. It extracts the color information and determines the appropriate brightness level and timing for each LED based on the received instructions.
●Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). To achieve different brightness levels for each LED, the IC uses Pulse Width Modulation. PWM involves rapidly turning the LED on and off with varying duty cycles, creating an illusion of different brightness levels for the human eye.
●RGB Color Mixing. The IC chip controls the individual Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) LEDs within each module. By adjusting the intensity of each color channel through PWM, the chip achieves a wide range of colors, allowing for stunning color-mixing effects.
●Timing and Synchronization. The IC chip relies on a precise timing mechanism to ensure that all LEDs on the strip change colors simultaneously and smoothly. Proper timing and synchronization are essential to avoid visual glitches and maintain a seamless color transition.
●Power Management. IC chips in addressable LED strips often incorporate power management features to ensure efficient energy use. They regulate the power supply to the LEDs, optimizing brightness levels while minimizing power consumption.
●Compatibility and Protocols. IC chips adhere to specific communication protocols, such as WS2812, WS2813, or APA102, ensuring compatibility with various controllers and devices. These protocols define the data format and transmission speed, allowing seamless integration into different LED systems.
●Cascade and Daisy Chain. Some IC chips support cascade or daisy chain configurations, enabling multiple LED strips to be connected. In this setup, data signals pass through each IC, allowing synchronized control of multiple LED strips as a single, continuous display.
The IC chips in Addressable LED Strip Lights bring intelligence and versatility to lighting systems, enabling precise control, vibrant color displays, and captivating visual effects.
Their ability to process data, perform PWM, and individually address each LED module transforms simple LED strips into dynamic and interactive lighting solutions for various applications like decorative lighting, stage effects, signage, and more.
Common IC Chip Models in Addressable LED Strip Lights
VIDEO - The Difference of Various LED Strip IC Chip Models
●WS2812B IC Chip

The WS2812B IC chip is widely utilized in addressable LED strip lights and is part of the larger family of WS281x chips. It is a combination of RGB LEDs and a control circuit integrated into a single package.
VIDEO - How To Control WS2812B Individually Addressable LEDs
Each WS2812B chip can individually control one RGB LED, allowing for precise color and brightness adjustments for each LED module on the strip. The WS2812B chip relies on a one-wire communication protocol, making it compatible with various microcontrollers and lighting control systems.
Its ease of use, compatibility, and robust capabilities make it a popular choice for numerous lighting applications, from decorative displays to dynamic visual effects in theaters and concerts.
●WS2813 IC Chip

The WS2813 IC chip is a crucial component for individual addressing and control in addressable LED strip lights. In an addressable LED strip using WS2813 chips, each LED module contains a WS2813 chip, and each chip can control one RGB LED.
When data signals are sent from a microcontroller or controlling device, the WS2813 chip receives and processes the instructions. It then interprets the data to determine the desired color and brightness level for each RGB LED.
The chip employs Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to control the individual LEDs’ brightness, allowing for a wide range of color variations and dynamic lighting effects.
The WS2813 chip’s dual-signal wires version is particularly advantageous. In case of a signal break or pixel failure, the chip can continue transmitting the data, ensuring that the malfunctioning LED does not affect the overall lighting display. This feature provides fault tolerance, preventing disruptions in the LED strip’s performance and maintaining a seamless lighting experience.
SK6812 IC Chip

In addressable LED strip lights using SK6812 chips, each LED module integrates SK6812 chip and a 5050 LED package. Similar to the WS2813, the SK6812 chip is responsible for individual control of each RGB LED pixel in the strip.
The controlling process begins when data signals are received by the SK6812 chip. The chip then interprets the instructions to adjust the intensity of the red, green, and blue LEDs using PWM technology. By manipulating the duty cycles of these LEDs, the chip can produce a broad spectrum of colors and achieve smooth transitions between different hues.
The SK6812’s smart digital interface input ensures precise color representation, maintaining consistent and accurate colors across all LEDs in the strip. This makes it ideal for applications requiring high-quality and uniform lighting effects, such as decorative lighting, visual displays, and entertainment setups.
●APA102 IC Chip

The APA102 IC chip, also known as DotStar, represents another widely used option for addressable LED strip lights. Unlike the WS2812, the APA102 employs a two-wire communication protocol, enabling higher data transfer rates and more straightforward synchronization for large-scale LED installations.
This chip offers superior color consistency and refresh rates, making it ideal for applications where precise color control and smooth animations are essential.
Additionally, the APA102’s compatibility with SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) communication allows for more complex and customized lighting effects, making it a preferred choice for advanced lighting projects, artistic installations, and professional stage lighting.
TM1814 IC Chip

Addressable LED strip lights utilizing TM1814 chips benefit from a four-channel LED constant current adjustable driver. The TM1814 chip is designed to work in tandem with a microcontroller, which provides data sets for each LED module on the strip.
Once the MCU inputs a group of data with constant current and PWM settings for the TM1814, the chip processes the data to control the RGB LEDs’ brightness and color output accordingly. The TM1814’s internal control synchronizing capability ensures that the colors and lighting effects remain synchronized across multiple LED strips if they are daisy-chained together.
With its integrated LED constant current driver circuit, the TM1814 provides consistent and stable current to the LEDs, ensuring uniform brightness and color accuracy throughout the strip.
Conclusion
The IC in addressable LED strip lights revolutionizes the way we experience and control illumination. From empowering individual pixel manipulation to creating mesmerizing color-changing effects, this intelligent technology opens up a world of possibilities.
By being well-equipped with the functionality of IC in addressable LED strip lights and exploring the common models, we unlock the artistry of dynamic lighting displays.