Voltage drop affects the brightness and performance of LED strips, especially in long installations. Understanding how to prevent it ensures optimal LED strip functionality.
Voltage drop refers to the gradual decrease in voltage along the length of an LED strip, leading to uneven brightness. Using thicker wires, shortening thestrip, or adding power injection points can help prevent voltage drop and maintain consistent brightness across the strip.
1. Why Does Voltage Drop Occur in LED Strips?
Voltage drop typically occurs in longer LED strips and when inadequate power supply or wiring is used. As current flows through the strip, the resistance in the wiring and the LEDs themselves causes the voltage to decrease, particularly at the strip’s far end. This results in noticeable dimming and color inconsistency in LEDs further from the power source.

The LED strip voltage drop formula can be used to estimate the voltage loss:
Voltage Drop (V) = Current (A) × Resistance (Ω) × Length (m).ds
Alternatively, an LED strip voltage drop calculator can simplify this process, providing quick and accurate estimations to adjust your installation.
2. How Do You Check LED Strip Voltage?
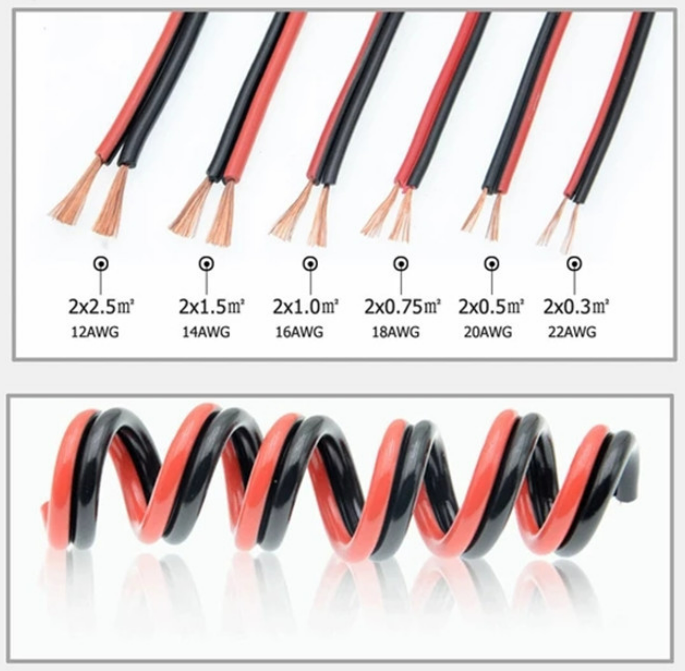
Checking the voltage in an LED strip is straightforward using a multimeter. Measure the voltage at the power source and at the far end of the strip. If there is a significant difference between the two, this indicates a voltage drop. Monitoring voltage drop is especially important in strips that use high current, as the LED strip wire gauge also plays a key role. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) reduce resistance and, therefore, voltage drop.
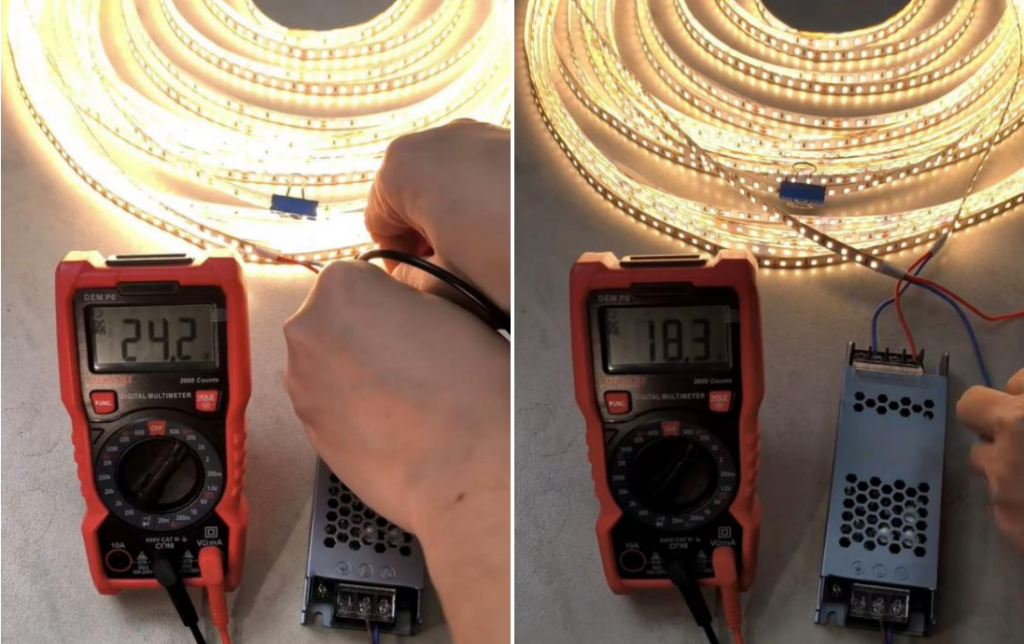


3. How to aviod voltage drop when wiring LED Strips?
Use Shorter Runs: Keep the length of each LED strip segment as short as possible. Longer runs of LED strips increase resistance, leading to voltage drop.
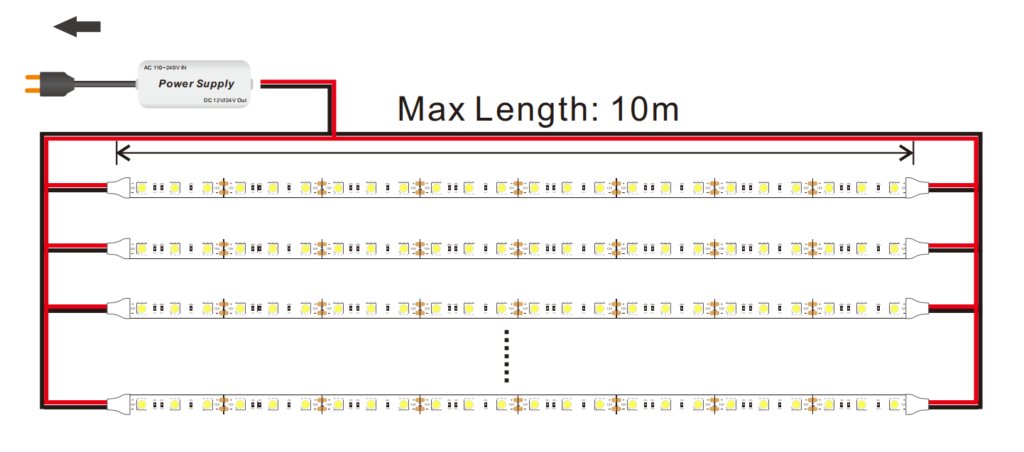
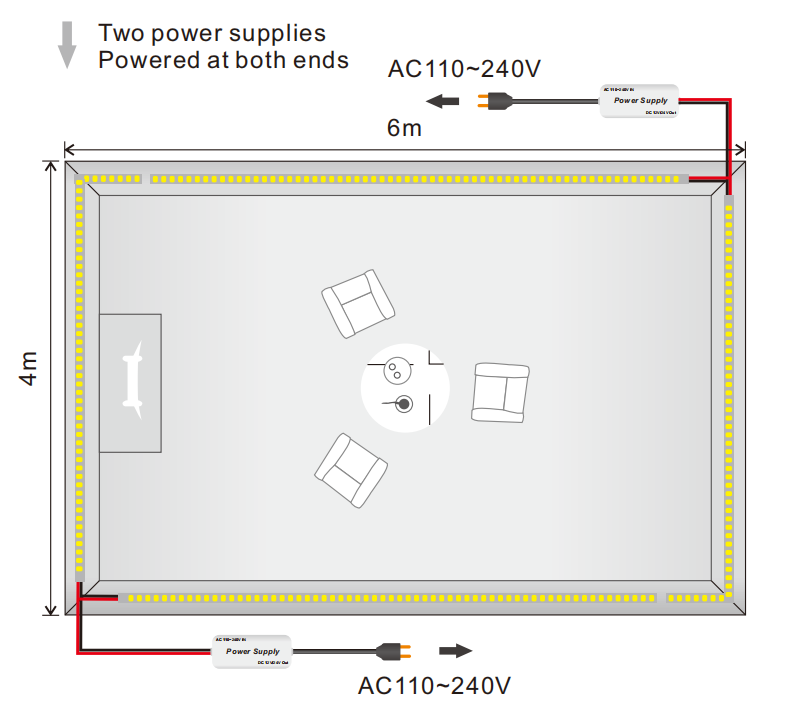
Power Injection: For longer runs, inject power at multiple points along the strip, such as at both ends or at intervals. This ensures consistent voltage and brightness.
Use Thicker Wires: Utilize thicker wires with lower gauge numbers (e.g., 16 AWG or 14 AWG) to minimize resistance and voltage loss.
Choose the Right Power Supply: Make sure the power supply matches the voltage requirement of the LED strip (e.g., 12V or 24V). Higher voltage systems (24V over 12V) typically experience less voltage drop over long runs.
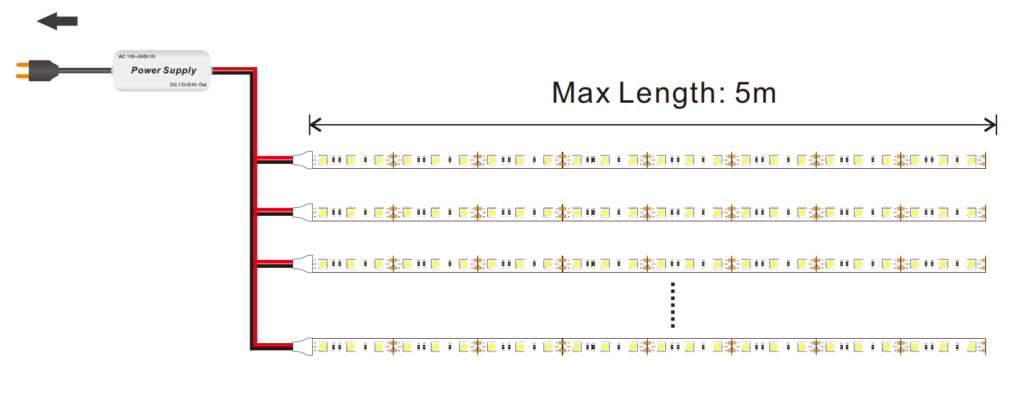
Parallel Connections: Connect multiple shorter LED strip segments in parallel to the power supply rather than wiring them in a continuous series.
4. How to Calculate Voltage Drop in LED Strips?
To calculate voltage drop, you need the current (measured in amps) and the resistance of the wire or LED strip (measured in ohms). Using the voltage drop formula mentioned earlier, you can determine the exact voltage loss over a given distance. For instance, the voltage drop for a 24V LED strip can vary depending on the wire gauge and length of the strip, making it essential to plan installations carefully to avoid brightness loss at the strip’s end.
5. What Happens If Voltage Is Too Low for LED?
When the voltage is too low, LED strips won’t operate optimally. The most common symptoms of low voltage include dimming, flickering, or color distortion. For example, a white LED voltage drop can cause the light to appear yellowish or faint, as the diodes can’t operate at full capacity. Extended exposure to low voltage can also shorten the lifespan of LEDs.
6. What is the Minimum Voltage Required for LED?
Most LEDs have a minimum voltage requirement to function correctly. For typical LED strips, this ranges from 2V to 3V per LED. For 24V LED strips, ensuring that the voltage remains above 20V is crucial for consistent brightness across the strip. Reference tools like an LED voltage drop chart can help you determine the correct power supply needed for different LED colors and voltages.
7. Can You Run 12V LEDs on 5V?
No, you cannot run 12V LED strips on a 5V power supply. LEDs require a specific voltage to work correctly, and a mismatch can result in malfunction or failure. For example, a 5V LED strip cannot provide the same brightness and power handling as a 12V strip, so trying to operate a 12V LED strip on 5V will result in very dim light or no light at all.
8. Is 5V Enough for a LED Strip?
5V LED strips are generally used for smaller installations and are typically less bright than higher voltage strips. These strips are ideal for low-power applications but are not recommended for larger areas because the lower voltage limits the number of LEDs that can be powered without significant voltage drop.
9. Are 12V LED Strips Brighter than 5V?
In general, 12V LED strips are brighter than 5V strips, especially over longer distances. This is because higher voltage strips can power more LEDs without experiencing the same voltage drop issues that are common with lower voltage strips. Higher voltage reduces current demand, minimizing the effect of resistance in the wiring.
10. Do 12V LED Strip Lights Get Hot?
While 12V LED strips can generate some heat, they do not typically become dangerously hot if properly installed. Good ventilation and proper power management ensure that the strips operate within safe temperature limits. However, excessive current can cause overheating, so always check that the strip’s power requirements align with your power source and consider using a suitable wire gauge to dissipate heat more effectively.
11. How Long Can You Run 12V LED Strip?
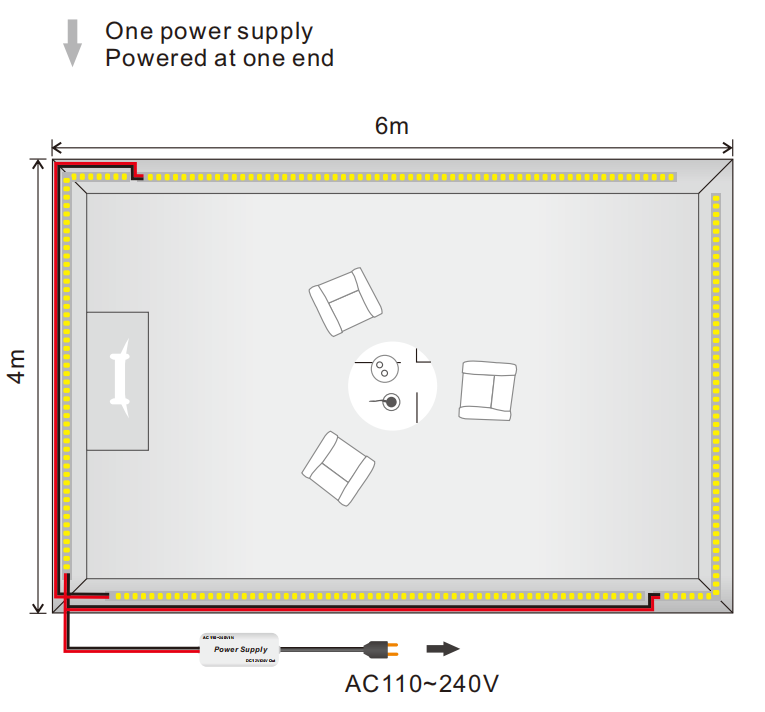
The recommended maximum run length for a 12V LED strip is usually around 5 meters (16.4 feet). Beyond this length, voltage drop becomes significant, and the LEDs at the far end may become noticeably dim. Using power injection at intervals or shortening the strip can reduce this issue, allowing for longer runs without sacrificing brightness.
12. Does a 12V LED Strip Need a Resistor?
Most 12V LED strips come with built-in resistors to regulate current. However, for DIY projects or if you are working with individual LEDs rather than pre-made strips, a resistor may be needed to protect the LEDs from receiving too much current and burning out.
Conclusion
Voltage drop is a common issue in LED strips, but it can be effectively managed through careful planning and the right equipment. Selecting the proper power supply, wire gauge, and installation method ensures your LED strips deliver consistent brightness and longevity.






